STERILISATION
Definition: Sterilization is the procedure of complete destruction (Killing) of all microorganisms present in a system. A product free from living microorganisms is called a “sterile product”.
- Antiseptic: Antiseptic substance stops the growth of microorganisms by preventing their action without destroying them is called antiseptic.
- Bactericide: The substance that kills bacteria is named as “Bactericide”.
- Bacteriostatic: Bacteriostatic refers to a chemical that stops or slows bacterial growth.
- Disinfection: A procedure that removes the infection likely by destroying microorganisms but not usually bacterial spores.
- Germicide: A material, but not necessarily bacterial spores, that kills harmful germs.
- Viricide: It is a substance that kills viruses.
- Sterility: The absence of viable microorganism is called ‘sterility’ & preparation free from viable microorganisms are called ‘sterile’.
THERMAL RESISTANCE OF MICROORGANISMS
- The microorganism show variable resistance to different Methods.
- Thermal death time: It can be described as the length of time needed to eradicate a certain type of microbe under particular circumstances and at a specified temperature.
- Death rate of microorganisms: There is no direct technique to determine when the sterility will be completed.
- Decimal reduction time (D value): It is defined as the time in min. required to decrease the number of the viable organisms by 90%.
- The order of death of microorganisms can be calculated from equation:
K = 1/t (log No.— log N)
Where,
- K stands for constant which depends on organism, temperature and medium.
- t is time of exposure in min.
- No stands for number of organisms viable at the beginning of a time interval.
- N=Number of organisms still viable at the end of the period.
K= 1/t
- As, it is after 90% reduction in microorganism.
- The D value, often known as the decimal reduction time, is defined as time t.
D= 1/K
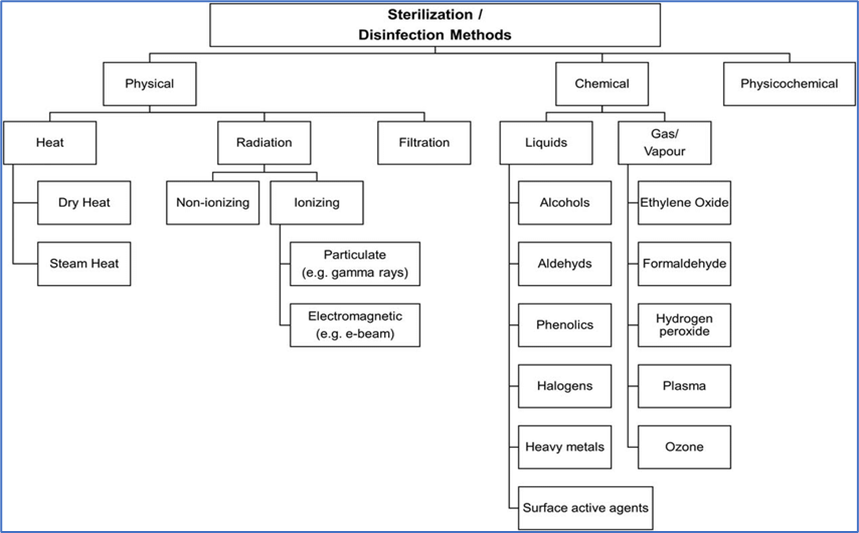
METHODS OF STERILISATION
- Physical Methods
- Dry Heat Sterilization
- Moist Heat Sterilization
- Radiation Sterilization
- Use Of Ultra Violet Rays
- Ionising radiation
- Chemical Methods:
- Sterilization by heating with bactericide.
- Gaseous Sterilization.
- Mechanical Methods: It includes the filtration of parenteral preparation through the following bacteria proof filters:
- 1. Ceramic filters
- 2. Seitz filter
- 3. Sintered glass filters
- 4. Sintered metal filters
- 5. Membrane filters

Reference:
- Sterilization of hydrogels for biomedical applications: A review: STERILIZATION OF HYDROGELS
- Sterilization (microbiology) – Wikipedia
- https://www.cdc.gov/infectioncontrol/guidelines/disinfection/sterilization/index.html
