What is In-Vitro-Fertilization (IVF) ?
Definition of In vitro fertilisation (IVF): It is a method of fertilisation in which an egg and sperm are joined in a laboratory setting. The procedure entails tracking and promoting a woman’s ovulatory cycle, taking an ovum or ova from her ovaries, and allowing sperm to fertilise her in a laboratory culture medium.
History of In-Vitro-Fertilization (IVF)?
1st Child after IVF treatment: Louise Brown (Year: 1978) (as a result of natural cycle IVF, no stimulation was performed)
Place: Dr. Kershaw’s Cottage Hospital (now Dr Kershaw’s Hospice) in Royton, Oldham, England (UK)
Notable things: Sir Robert G. Edwards was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2010,
Why IVF is preferred? Or What Causes of Infertility Can IVF Treat?
In vitro fertilisation (IVF) is a method of treating infertility and genetic disorders. If IVF is used to treat infertility, male and female may be able to try less intrusive treatment options first, such as fertility medicines to boost egg production or intrauterine insemination (IUI), a procedure in which sperm are implanted directly into the uterus near ovulation.
IVF is mainly offered as a primary treatment for infertility in women below age 40. IVF can be option for below condition:
- Fallopian tube damage or blockage
- Ovulation disorders
- Endometriosis
- Uterine fibroids
- Low sperm counts
- Poor egg quality
- Previous tubal sterilization or removal
- Impaired sperm production or function
- Unexplained infertility
- Antibody problems that harm sperm or eggs
- A genetic disorder arise from parental gene
- Fertility preservation for cancer or other health conditions: In such case, the patient is going to start cancer treatment which may lead to infertility. Preservation of eggs or sperm is stored for IVF treatment.
- Women who don’t have a functioning uterus or for whom pregnancy poses a major health risk may choose IVF and have the baby carried by someone else (gestational carrier). The woman’s eggs are fertilised with sperm in this situation, but the resulting embryos are implanted in the uterus of the gestational carrier.
Read More on:
What are the Risks associated with In-Vitro-Fertilization (IVF) ?
Risks of IVF include:
- Multiple births: IVF increases the risk of multiple births if more than one embryo is transferred to patient uterus.
- Premature delivery and low birth weight
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: Due to usage of injectable fertility drugs, like as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), to induce ovulation which leads to ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Symptoms include: ovaries becoming swollen and painful. Rarely rapid weight gain and shortness of breath.
- Vomiting, diarrhea, Mild abdominal pain, bloating & nausea.
- Miscarriage: About 15% to 25%, but the rate increases with maternal age.
- Egg-retrieval procedure complications: Using aspirating needle to collect eggs may lead to bleeding, infection or damage to the bowel, bladder or a blood vessel.
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Birth defects
- Cancer
- Stress
What is In-Vitro-Fertilization (IVF) process step by step?
Understanding the Steps of IVF:
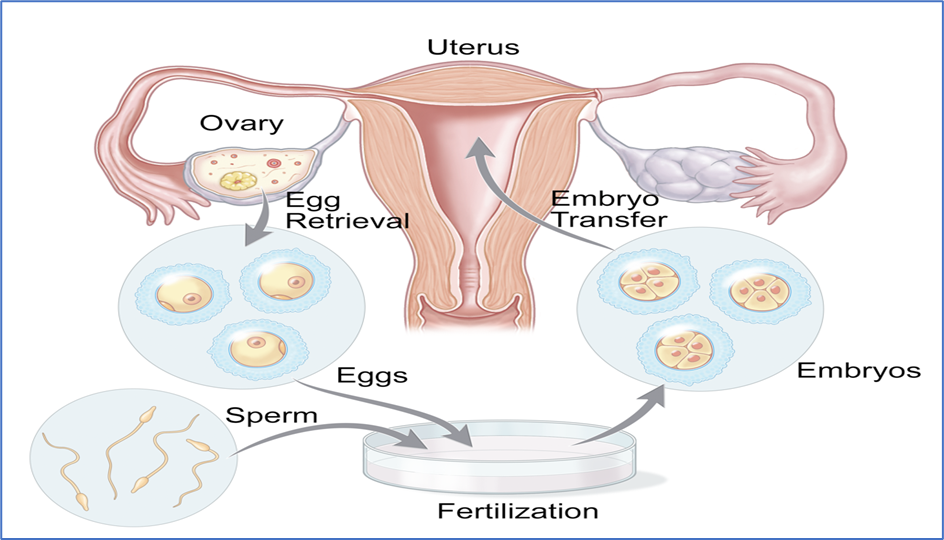

Step 1: Testing and Ovarian Stimulation
- The candidate must undergo a uterine and fallopian tube test before beginning the IVF process. This is necessary to ensure that there are no new issues that will require surgical intervention.
- Pre-cycle testing can detect this, which involves hormonal examination to measure thyroid function and ovarian reserve, sexually transmitted infection screening for both couples, and male partner semen analysis.
- Women: She took fertility medicines for 8-14 days for ovarian stimulation.
- For egg retrieval, ovarian stimulation is employed to mature eggs.
- Because not all mature eggs are viable for use in the IVF process, egg retrieval requires 10-20 mature eggs.
Step 2: Egg Retrieval
- The eggs will be removed from follicles in the ovaries during surgery. Before the eggs ovulation, this operation is conducted 34-36 hours after receiving the trigger injection.
- Egg retrieval is done with a needle under the supervision of transvaginal ultrasonography.
- The embryologist scans the follicular fluids for all accessible eggs.
- Because she will be sedated, the patient will not feel any pain during the procedure. Following that, the contents of the follicular fluid are removed using mild suction, which moves the egg along in the fluid.
- The follicular fluid will be collected in a small test tube and handed to the embryologist.
- The eggs are cultured in an incubator in a specific media until they are inseminated. It takes hardley 30 minutes to complete this operation.
Step 3: Fertilisation
- Under Fertilisation step, about 50,000 to 1,00,000 motile sperm are transported to the dish containing the eggs, called standard insemination.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) technology is used to fertilize mature eggs. A high-power microscope is being used to perform this fertilisation.
- The embryologist next uses a fine glass microneedle to pick up a single spermatozoon and inject it directly into the egg cytoplasm.
- Fertilization is reviewed 16 to 18 hours after ICSI. After that, the zygotes are cultured in a special culture medium that ropes their development.
- On the second and third days following retrieval, zygotes are evaluated.
Step 4: Embryo Transfer
- Embryo Transfer is the next phase, which involves returning fertilised eggs to a woman’s uterus or fallopian tubes. This might happen anywhere from 1-6 days after the egg removal.
- Based on the rate of development and look of the embryos, the embryologist and doctor will determine when to perform embryo transfer, as well as which and how many embryos should be transferred.
- When the eggs are at the cleavage stage, they will be transferred on the third day, and when they are at the blastocyst stage, they will be transplanted on the fifth day. Embryo transfer is a relatively painless procedure. The eggs are inserted in a soft catheter and passed through the cervix into the uterine cavity.
Step 5: Assisted Hatching
- This procedure is usually performed on elderly women who have frozen or thawed embryos. A hole must be formed in the flexible shell that surrounds the cells of the early embryo in this step, which requires micromanipulation. Before the embryo transfer, this step is carried out.
Step 6: Pregnancy Test
- The doctor will usually do a blood pregnancy test 12 days following the embryo transplant to confirm the pregnancy.
- If the pregnancy is confirmed, blood tests and ultrasounds will be performed on the candidate. The candidate will be referred back to the obstetrician if the pregnancy appears to be normal.
What are the costs of IVF?
What is the cost of IVF in USA?
- According to the National Conference of State Legislatures, the average cost of an IVF cycle in the United States is between $12,000 and $17,000.
- This price will vary conditional on where you live, the number of medications you’re required to take, and the number of IVF cycles you undertake.
What is the cost of IVF in India?
- An IVF cycle might price anywhere around Rs 2.5 lakhs and Rs 4 lakhs on average.
- Additional drugs and testing may be required, as well as procedures like as Frozen Embryo Transfer, which can drive up the price.
What is the IVF success rate?
- In India, the success rate of IVF ranges from 30 to 35 percent, depending on the conditions mentioned above. In young women, the average IVF success rate is around 40% worldwide. Women under the age of 35 have a higher likelihood of success than older women.
What are the alternatives to In-Vitro-Fertilization (IVF)?
- Artificial insemination:
- Intracervical insemination (ICI)
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- Intravaginal insemination (IVI) of semen.
- Benefit of Artificial insemination:
- It requires that a woman ovulates, but is a relatively simple procedure, and can be used in the home for self-insemination without medical practitioner assistance.
- Women who want to have their own kid but are single, women in a lesbian partnership, or females in a heterosexual relationship but with a male partner who is infertile or has a physical handicap that prevents full intercourse from taking place benefit from artificial insemination.
- Ovulation induction drug or treatment is an alternative for women with anovulation or oligoovulation,
- Surrogacy
- Adoption
What is anovulation?
- When an egg (ovum) does not release from your ovary during your menstrual cycle, this is known as “Anovulation”.
What is Oligoovulation?
- It’s a disorder that generates uneven or irregularly spaced periods. Women who have an ordinary menstrual cycle have periods every 28 to 32 days, but women who have oligoovulation have eight or fewer periods per year.
What is Intrauterine insemination (IUI)?
Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a form of artificial insemination used to treat infertility. The woman is injected with specially prepared sperm during this process. Prior to IUI, the woman may be given medications that induce ovulation.
IUI is frequently used to treat infertility.
- Mild male factor infertility
- Women who have problems with their cervical mucus
- Pateners with unexplained infertility
What is Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)?
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) is a term that refers to a variety of techniques used to assist infertile couples.
ART works by extracting a woman’s eggs from her body. Embryos are formed by mixing the eggs with sperm. The embryos are then re-implanted into the woman’s body.
Read More:
For More Health Topic Click Here
Analytical Development Topic Click Here,
Formulation Development Topic Click Here,
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In_vitro_fertilisation
https://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/guide/in-vitro-fertilization
https://www.womenshealth.gov/a-z-topics/infertility
