HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus
AIDS: Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome
What is HIV and AIDS?
HIV and AIDS: Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. Untreated HIV can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency syndrome).
There is currently no effective cure. Once people get HIV, they have it for life.
But with proper medical care, HIV can be controlled.
What are the Symptoms?
Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches and joint pain
- Rash
- Sore throat and painful mouth sores
- Swollen lymph glands, mainly on the neck
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Cough
- Night sweats
- Swollen lymph nodes — often one of the first signs of HIV infection
- Oral yeast infection (thrush)
- Shingles (herpes zoster)
- Pneumonia
What are the Causes?
HIV is caused by a virus. It spread through sexual contact or blood, or from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breast-feeding.
How does HIV become AIDS?
HIV destroys CD4 T cells — white blood cells that play a large role in helping body to fight against disease. The fewer CD4 T cells you have, the weaker your immune system becomes.
How HIV spreads?
- By having sex
- By contaminated /sharing needles
- From blood transfusions
- During pregnancy or delivery or through breast-feeding
How HIV doesn’t spread?
HIV or AIDS cannot be spread by hugging, kissing, dancing or shaking hands with someone who has the infection.
HIV isn’t spread through the air, water or insect bites.
Who is at risk for HIV infection?
Anyone can get HIV, but certain groups have a higher risk of getting it:
- People who have another sexually transmitted disease (STD). Having an STD can increase your risk of getting or spreading HIV.
- People who inject drugs with shared needles
- • Gay and bisexual men, especially those who are Black/African American or Hispanic/Latino American
- People who engage in risky sexual behaviours, such as not using condoms
Complications with HIV
HIV infection weakens your immune system, making you much more likely to develop many infections and certain types of cancers.
Common Infections to Patients:
- Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP).
- Candidiasis (thrush)
- Tuberculosis (TB).
- Cytomegalovirus: It is a herpes virus is transmitted in body fluids such as saliva, blood, urine, semen and breast milk. A well-defined immune system inactivates the virus, and it remains inactive in your body. If your immune system compromised with HIV, the virus resurfaces — causing damage to your eyes, digestive tract, lungs or other organs.
- Cryptococcal meningitis: Meningitis is an inflammation of the membranes and fluid surrounding your brain and spinal cord (meninges). Cryptococcal meningitis is a common central nervous system infection associated with HIV, caused by a fungus found in soil.
- Toxoplasmosis: This potentially deadly infection is caused by Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite spread primarily by cats. Infected cats pass the parasites in their stools, which may then spread to other animals and humans. Toxoplasmosis can cause heart disease, and seizures occur when it spreads to the brain.
- Cancers common to HIV/AIDS
A. Lymphoma: This cancer starts in the white blood cells (Blood Cancer).
B. Kaposi’s sarcoma: A tumor of the blood vessel walls, Kaposi’s sarcoma usually appears as pink,
red or purple lesions on the skin and mouth.
- Wasting syndrome: Untreated HIV/AIDS can cause significant weight loss, often accompanied by diarrhoea, chronic weakness and fever.
- Neurological complications: HIV can cause neurological symptoms such as confusion, forgetfulness, depression, anxiety and difficulty walking. HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders (HAND) can range from mild symptoms of behavioural changes and reduced mental functioning to severe dementia causing weakness and inability to function.
- Kidney disease: HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN) is an inflammation of the tiny filters in your kidneys that remove excess fluid and wastes from your blood and pass them to your urine.
- Liver disease: Liver disease is also a major complication, especially in people who also have hepatitis B or hepatitis C.
What are the Prevention of HIV and AIDS?
There’s no vaccine to prevent HIV infection and no cure for AIDS. But you can protect yourself and others from infection.
- Preferred treatment as prevention (TasP).
- Use post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) if you’ve been exposed to HIV.
- Use a new condom during sex.
- Consider preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP).
- Tell your sexual partners if you have HIV.
- Use a clean needle.
- If you’re pregnant, get medical care right away.
- Consider male circumcision.
- General Awareness
Treatments of HIV and AIDS:
Currently available Drugs as below table:
| Compound | Innovators |
| Combinectin | ViiV Heathcare |
| Cabotegravir | ViiV Healthcare |
| Mk-8504 / mk-8583 | Merck/MSD |
| Bnabs: including 3BNC117 and 10-1074; PGDM1400 and PGT121, 10E8. | Various including NIH/NIAID, Rockefeller University, ViiV Healthcare, Gilead Sciences. |
| Islatravir | Merck/MSD |
| GS-6207 (capsid) | Gilead Sciences |
| GSK ’937 (maturation) | ViiV Heathcare |
| elsulfavirine | Viriom |
Vaccine Trials for HIV and AIDS:
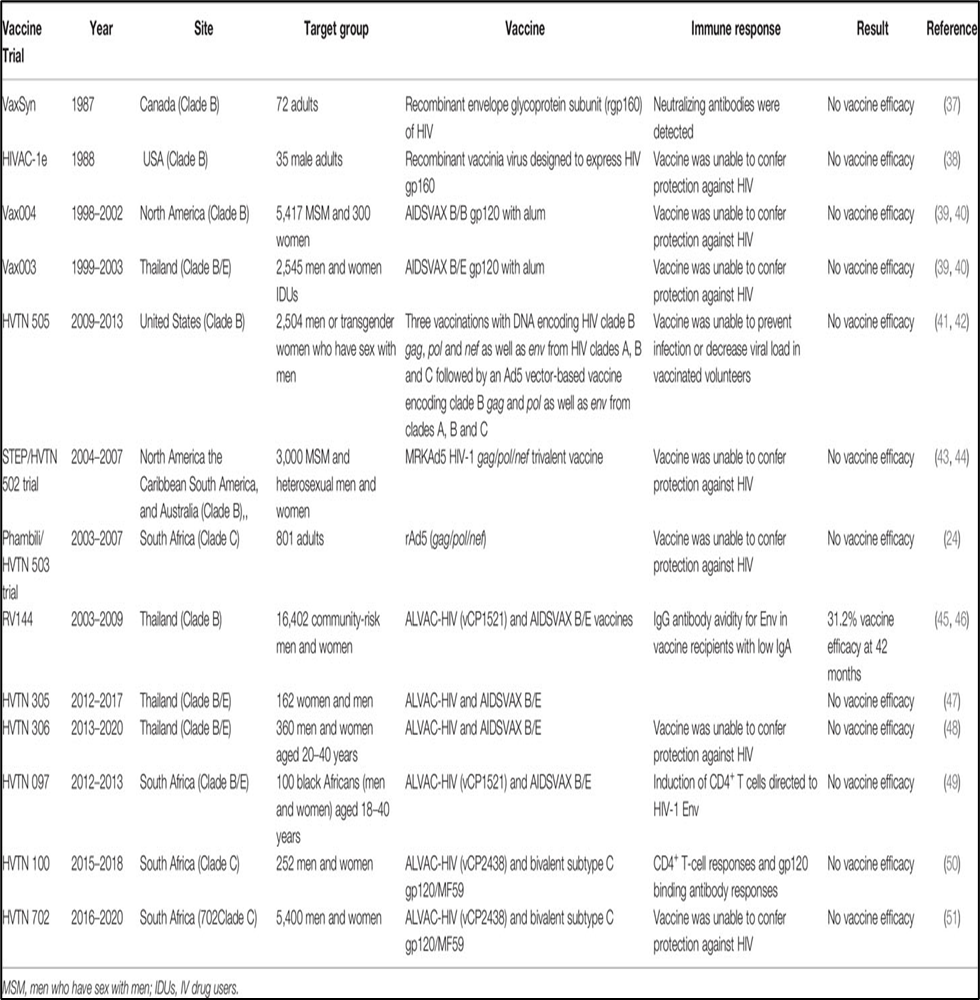

(Credit: frontiersin.org)
Currently:
Moderna, Gilead, Johnson & Johnson are in race with development of HIV vaccine.
- The US Military’s HIV Research Program (MHRP)
- HIV Vaccine Trials Network
- The International AIDS Vaccine Initiative (IAVI)
Other NGO are involved to cure HIV in world.
World AIDS Day:
1 December every year since 1988, It is an international day dedicated to aware about the AIDS pandemic and spread of HIV infection in human beings. Also to mourning those whom we lost of the disease
Read More:
CPOD: https://pharmasciences.in/explore/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-copd/
Breast Cancer: https://pharmasciences.in/explore/breast-cancer/
Reference:
frontiersin.org

