What is a Migraines and Migraine headache?
A migraine is a common neurological disease or headache that causes a variety of indications on any one side of the head, that includes,
- Pulsating
- Throbbing
- Perforating
- Pounding
- Debilitating
Migraine may be worsened with physical actions, lights, sounds, or smells. It could be persist for at least hours or even days.
Definition:
Throbbing:
Throbbing is a pulsing, beating sensation that happens over and over again. Its outcomes from the dilation of patient blood vessels from the increased blood flow in body.
Pounding :
It is a condition where patients feel rhythmical beating.
Debilitating :
A condition where a body may feel very weak and infirm.
Symptoms with Phases of Migraines
| Sr. No. | Name of Stage | Symptoms | Remarks |
| 1 | Prodrome stage | Food cravings Depression Fatigue or low energy Too Frequent yawning Hyperactivity Irritability Neck stiffness | 3 hr to Several days of headache. |
| 2 | Migraine with Aura | Problem in speaking Feeling an irritation or burning sensation in your face, arms, or legs Hallucination of shapes, light flashes, or bright spots Temporarily not properly vision Ringing in any ears Minor changes in touch, smell, or taste | 5- 60 min of headache. |
| 3 | Attack (Headache) | Pain usually on one side of your head, but often on both sides Pain that throbs or pulses Light, sound, and may time smell and touch sensitivity Nausea and vomiting | 4 to 72 hr of duration of Headache. |
| 4 | Postdrome (Also called this migraine as “Hangover”) | Heavy tiredness. Unusually refreshed or happy Pain in muscle or weakness Cravings or lack of appetite for food Unable to concentrate. | May stay a few hours to more than a day after the headache goes away |
Types of Migraines
- Migraine with aura (complicated migraine)
- Migraine without aura (common migraine)
- Migraine without head pain (It is also known as “Silent migraine” or “Acephalgic migraine”)
- Retinal Migraine or Ocular Migraine or Optical Migraine: It is a temporary, partial, or complete loss of vision in one of the patient eyes, with a dull pain behind the eye that could spread to the rest of patient’s head. That vision loss could be for a minute or could be for months.
- Chronic Migraine: This type of migraine occur at least 15 days in a month. The signs may change frequently and severity of the pain change in patient.
- Migraine with Brainstem Aura: This migraine includes vertigo, slurred speech, double vision, or loss of balance, which happens before the headache. These symptoms may lead to an inability to speak correctly, ringing in the ears, and vomiting.
- Status Migrainosus: This type of migraine may occur upto 72 hours. Patients may feel headache pain and nausea extremely bad.
- Vestibular Migraine: It is a nervous system issue that causes recurrent dizziness or vertigo-like condition in a person having a history of migraine symptoms. Vestibular Migraine may not always have a headache.
- Hemiplegic Migraine: Hemiplegic migraine is a rare illness in which a migraine headache comes along with weakness on one side of the body (hemiplegia). Patients may describe as having a migraine with aura.
Some of the medications, or medication withdrawal, may leads to this type of migraine.
What reasons for Migraine?
- Bright lights
- Severe heat, or other extremes in weather
- Dehydration
- Barometric pressure Changes or Weather changes
- Hormone changes (Example are female at birth, like estrogen and progesterone fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause)
- Excess stress
- Loud sounds
- Intense physical activity
- Skipping meals
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Medications, like oral contraceptives or nitroglycerin.
- Unusual smells
- Stress
- Certain foods & their additives: Like Old cheeses and salty and treated foods, sweetener -aspartame & the food-preservative monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Smoking
- Alcohol use
- Traveling
- Drinking alcohol, Wine, and too much caffeine (Mostly coffee).
What are the Risk factors that may trigger Migraine?
- Family history.
- Age: Migraines may start at any age. Migraines possibility higher during your 30’s, and slowly become less severe and less recurrent in the later years.
- Sex: Women are 3 time more possible than men to have migraines.
- Hormonal changes: Menstruation, Pregnancy & Birth control may lead to migraines. It will be improved after menopause.
Treatment of Migraine or How to get Migraine relief ?
| Sr. No. | Severity Stage | Drugs | Remarks |
| 1 | Acute or Abortive medications | 1. NSAIDs: ibuprofen or aspirin 2. Triptans: Sumatriptan, eletriptan, and rizatriptan. 3. Antiemetics: Metoclopramide, chlorpromazine, and prochlorperazine. 4. Ergot alkaloids: Migranal and Ergomar 5. Lasmiditan 6. CGRP receptor antagonists: Rimegepant or Ubrogepant | Very effective when patients use them at the first sign of a migraine. |
| 2 | Preventative or Prophylactic medications | 1. Antihypertensives: Helpful for high blood pressure and may also help with migraine attacks. Beta-blockers Angiotensin receptor blockers (candesartan) 2. Anticonvulsants: Some of anti-seizure medications may help to prevent migraine attacks. 3. Antidepressants: Amitriptyline and venlafaxine, 4. Botox: It is a drug prepared from a toxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum Botox injections are administered to the head and neck muscles every 3 months. 5. Calcitonin gene-related peptide treatments 6. Single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation (sTMS) 7. Neuromodulation devices. | This type of medication is prescribed when migraine are severe or occurrences are more. |
Excedrin Migraine (OTC Drug)
Excedrin is an over-the-counter (OTC) headache pain reliever, a combination of aspirin, acetaminophen, and caffeine.
It was first manufactured by Bristol Myers Squibb.
it was sold to Novartis than GSK.
Named as Anadin Extra in UK.
Daith piercing’s effective for Migraines
There is no research based evidence to support saying that a daith piercing may provide relief from migraine episodes.
This therapy may support on bases that the piercing works as acupuncture. The point at which daith piercing is performed, it crossed by the vagus nerve.
Prevention of Migraine or Remedy of Migraine
- Take a rest with eyes closed in a dark, quiet room
- Cool compress or ice pack put on forehead & rest
- Drinking plenty of liquids and minerals
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT).
- Supplements: Some supplement includes vitamins, minerals, and ancient herbs that can stop or treat migraines. These contain riboflavin, coenzyme Q10, and melatonin. Butterbur or Coltsfoots (Petasites hybridus) a shrub . It Could help to head off migraines, may affect your liver enzymes.
- Avoid drinking
- Avoid Tobacco
- Avoid too much coffee.
- Avoid stress and Relaxation your body with meditation, yoga, and mindful breathing will help.
Difference between Tension Headache, Sinus Headache and Migraine Headache.
| Tension Headache | Sinus Headache | Migraine |
| It is emotional, mental, or physical stress that occur in human. | Pain with a runny or stuffy nose is the very likely symptom of a sinus headache. | Headache on any one side of the head. |
| Patients may complain of a group of pain across their forehead or pressure on either side of the head. | Mucus to thicken and sometimes turn a yellowish color in this condition. | It affects the worse on one side of the head of the patients. Patients with migraine mucus is clear and runny. |
| It is not as severe as a migraine | NA | It is more severe than a Tension headache. |
| Resolved by OTC or taking a rest. | Treated with decongestants, antihistamines and sometimes antibiotics (in case of bacterial infection) | Need to go for a check-up. |
Type of headache
This includes Migraine headache, Tension Headache, Sinus Headache and Cluster headache.
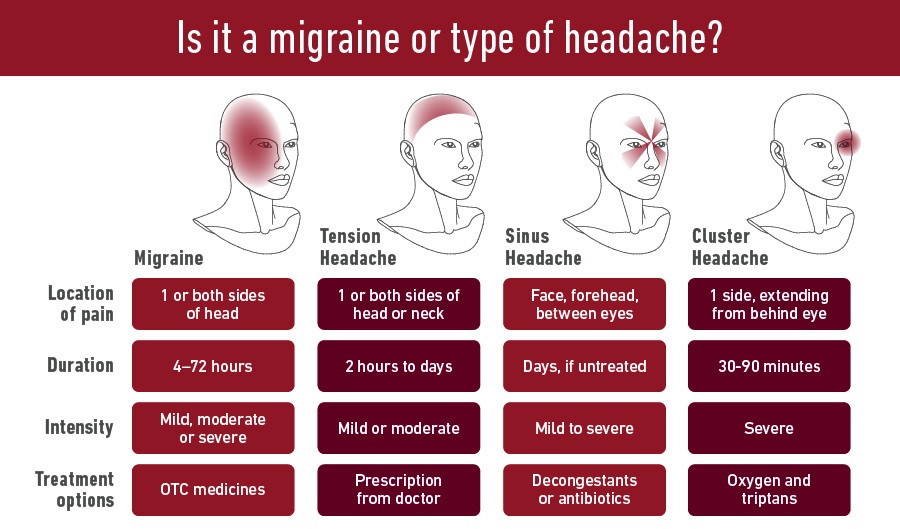

Credit: templehealth.org
Abdominal migraine (AM)
Abdominal migraine is not a headache. It is a common reason for chronic and repeated abdominal pain (around the belly button) in children.
Note: These articles are only for educational purposes. Consult your doctor for a better resolution.
References:
healthline.com/health/migraine#symptoms
webmd.com/migraines-headaches/migraines-headaches-migraines
