What is Data Integrity? & Why is it so Important?
What is data integrity?
- Definition of Data integrity: It is the inclusive of data consistency, accuracy, & completeness. It denotes to the safety and security of data in respect to regulatory compliance – such as GDPR compliance, FDA submission.
- It is kept up to date by a set of processes, regulations, and standards that were put in place thru the design phase.
- The info. consist in a database will stay accurate, complete & dependable no matter how long it is stored or how frequently it is accessed if it is protected and secured.
- The value of it, in avoiding data loss or leakage cannot be overstated, in order to keep electronic data safe from destructive outside influences, user must first ensure that internal users are treating data correctly.
- User may ensure that sensitive data is never miscategorized or stored wrongly by implementing suitable data validation and error checking, thereby exposing to potential risk.
Types of Data Integrity:
Preserving it needs an understanding of the two types of data integrity:
- Physical integrity
- Logical integrity.
1. Physical integrity:
- As name listed Physical integrity, it is the protection of the completeness and precision of that data as it’s stored and retrieved from physical memory drive.
- Physical integrity is affected when natural calamities hit, power goes out, or hackers interrupt database functioning.
- Data processing managers, system programmers, applications programmers, and internal auditors may be unable to access accurate data due to human mistake, storage erosion, and a variety of other difficulties.
2. Logical integrity:
- In a relational database, logical integrity safeguards that data remains complete when it is used in various ways. Data is also protected from human error and hackers by this things.
- Sub Type:
- Entity integrity: To confirm that data isn’t recorded more than once and that no field in a data-base is null, entity integrity relies on the generation of primary keys -the unique values that identify pieces of data. It’s a typical of relational systems, which save data in tables that could be linked and used in various ways.
- Referential integrity: It is refers to the series of methods that make definite data is stored & used uniformly. Database’s structure is Rules embedded so that how foreign keys are used confirm that only suitable changes, additions, or deletions of data performed. Rules can consist of restrictions that eliminate the entry of duplicate data, assurance that data entry is precise, and/or prohibit the entry of data that does not apply.
- Domain integrity: It is the collection of procedures that guarantee the accuracy of each part of data in a domain.
- User-defined integrity: User-defined integrity states to the rules and limitations that the user makes to meet their own requirements. Entity, referential, and domain integrity aren’t always enough when it arises to data security. Business rules must frequently be considered and included into its safeguards.
This principle is not applicable for
- It is not data security.
- Data integrity is not data quality
- Integrity and Regulatory compliance
Data integrity risks:
- Human error
- Transfer errors
- Bugs and viruses
- Compromised hardware
Procedure to reduce Data Integrity Risk
- Promote a work culture of Integrity awareness.
- Implement Quality Control measures in association with IT personnel to verify and monitor data.
- Periodical review and create an Audit Trail risk assessment.
- Prepare & implement process Maps for All Critical Data
- Remove known Security Vulnerabilities to benefit minimize integrity risks
- Software Development Lifecycle evaluation.
- Full proof Computer Validation Systems (CSV) implementation.
- Tool to minimize the Error-by-Error Detection Software and Anti-Virus software.
The Importance of Data Integrity
- In pharmaceutical manufacture and research, data has always been crucial. However, due to a variety of circumstances, the value of data is increasing at an exponential rate.
- Enhanced regulatory requirements, as well as changing customer and end-user expectations, as well as the pharmaceutical industry’s increasingly competitive nature, are driving this trend.
- The ALCOA principles confirm data integrity.
ALCOA apply to following types of GMP records:
- Electronically recorded
- Paper-based
- Hybrid: Including both paper based and electronic records create the original record
- Others : Like photography, chromatography plates, images, and weight prints etc.
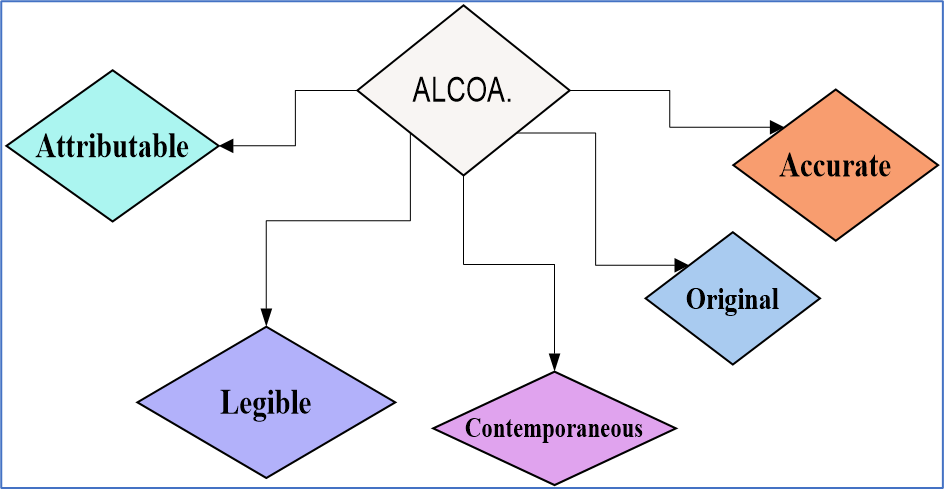
The ALCOA Principles :
The abbreviation ALCOA stands for the original five principles.
ALCOA principles are:
- Attributable
- Legible
- Contemporaneous
- Original
- Accurate
The original ALCOA principles, on the other hand, have since been modified to ALCOA+. (ALCOA plus). The original principles persist with four add-ons:
- Complete
- Consistent
- Enduring
- Available

For More on Click on : Definition, ALCOA++, GDP
Read More:
- Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
- Paper Chromatography
- Thin Layer Chromatography
- Difference Between Thin Layer and Paper Chromatography
- Type of Glass container used in Pharmaceuticals Fume Hood
- Type of HPLC Column Type of Capsules Advantages and Disadvantages of Capsules
- Gelatin
- Type of HPLC Detectors
- Difference between HPLC and UPLC
- What are the Differences between GC and HPLC?
Topic on :
