What is full form of HEPA Filter?
HEPA is a kind of mechanical air filter with pleats. High efficiency particulate air filter is represented by this acronym.
HEPA acronym has also three formal meanings as listed below,
- High-efficiency particulate air.
- High-efficiency particulate absorbing.
- High-efficiency particulate arrestance.
What is a HEPA filter?
- HEPA’s full name is “High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filter”.
- The US Department of Energy has given HEPA a formal definition.
- HEPA air filter’s Common standards require should remove particles from the air that passes through at least 99.95% (ISO, European Standard) or 99.97% (ASME, U.S. DOE)
- Theoretically, this kind of air filter can eliminate 99.97 percent or more of pollen, virus (0.02-0.3 μm), dirt, dust, moisture, bacteria (0.2-2.0 μm), and sub-micron liquid aerosol (0.02-0.5 μm).
- HEPA filters with photocatalytic oxidation can capture some bacteria like Aspergillus niger, Penicillium citrinum, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Bacillus subtilis (PCO).
- The worst-case scenario is addressed with the diameter specification of 0.3 µm; the Most Invasive Particle Size (MPPS).
- To function correctly, all air purifiers need regular cleaning and filter replacement. Follow the maintenance and replacement advice provided by the HEPA manufacturer.
- HEPA filters are utilised in settings where contamination control is necessary, including the production of hard disc drives, medical equipment, semiconductors, food, pharmaceutical, and nuclear items, as well as in homes, offices, and cars.
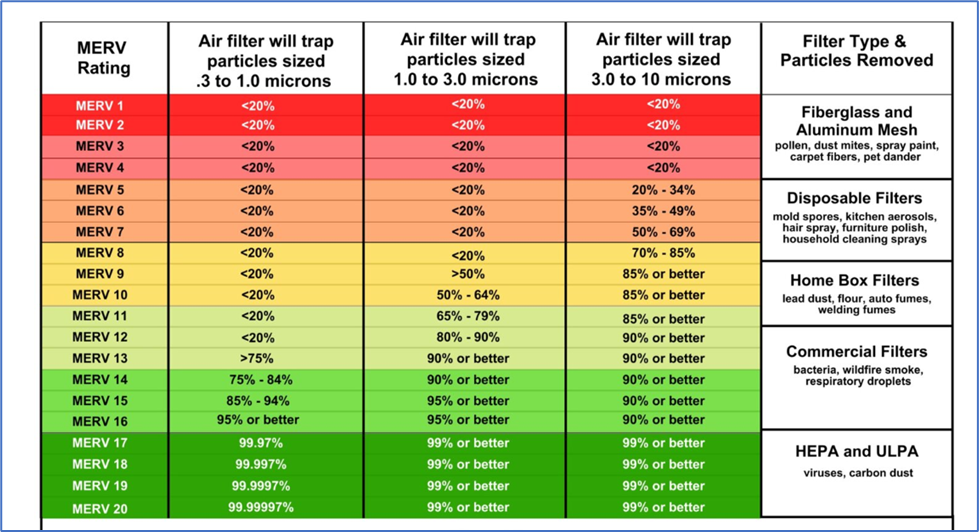
What is Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values (MERV) ?
Full form of MERVs is Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values. Value indicates its (filters) capacity to remove particles larger than 0.3 microns (µm).
- This value is valuable for evaluating how well certain filters perform.
- The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating, and Air Conditioning Engineers‘ test technique provides the basis for the rating (ASHRAE).
- The filter performs better at capturing particular sorts of particles the higher its MERV rating.
| MERV Rating | Average Particle Size Efficiency in Microns |
| 1-4 | 3.0 – 10.0 less than 20% |
| 6 | 3.0 – 10.0 49.9% |
| 8 | 3.0 – 10.0 84.9% |
| 10 | 1.0 – 3.0 50% – 64.9%, 3.0 – 10.0 85% or greater |
| 12 | 1.0 – 3.0 80% – 89.9%, 3.0 – 10.0 90% or greater |
| 14 | 0.3 – 1.0 75% – 84%, 1.0 – 3.0 90% or greater |
| 16 | 0.3 – 1.0 75% or greater |
Types of HEPA Filters?
- As a True HEPA filter, a HEPA-type filter, or just a plain old current HEPA filter. But there are important differences between them.
- Since it is certified to collect 99.97 percent of particles down to 0.3 microns in size, a true HEPA filter is essentially the best type. Compared to HEPA Types, True HEPA is more effective. HEPA filter efficiency range is 99.97%.
As per European Union standard
- The EN 1822 European Union standard, which applies to both HEPA and ULPA filters, divides filters into various classifications based on their efficacy.
- All EN 1822 requirements are based on a filter’s capacity to capture and hold the MPPS that is unique to that filter. Usually, a laser spectrometer or an electrostatic classifier is used to calculate the MPPS.
| Classification | Filter type | Percentage efficiency at MPPS |
| E10 | HEPA | ≥ 85 |
| E11 | HEPA | ≥ 95 |
| E12 | HEPA | ≥ 99.5 |
| H13 | HEPA | ≥ 99.95 |
| H14 | HEPA | ≥ 99.995 |
| U15 | ULPA | ≥ 99.9995 |
| U16 | ULPA | ≥ 99.99995 |
| U17 | ULPA | ≥ 99.999995 |
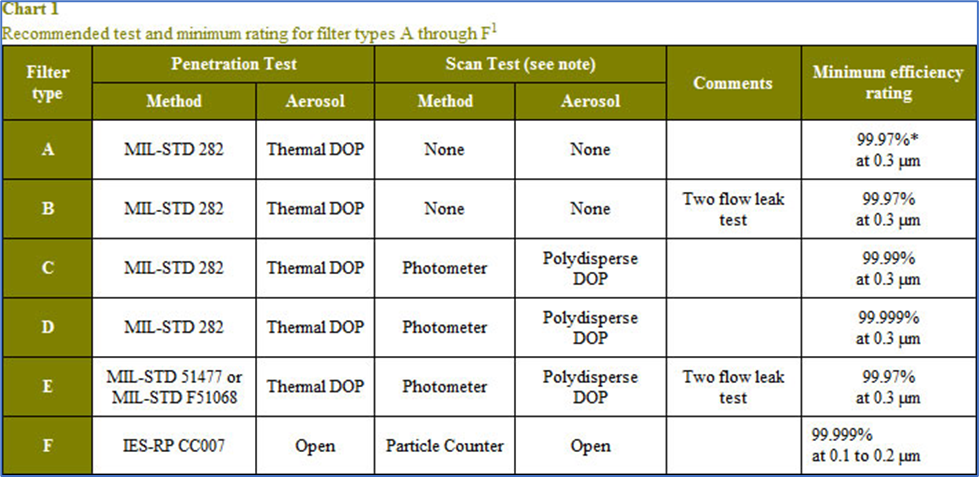
As per Institute of Environmental Science and Technology (IEST)
- There are six types of performance, categorized by the Institute of Environmental Science and Technology (IEST) as A, B, C, D, E, and F. According to chart 1 below, each has unique qualities of its own.
Marketing Traps in HEPA-Like
Be mindful of these marketing jargon terminology while purchasing HEPA filters.
- “HEPA-type”.
- “HEPA-like”.
- “HEPA-style”.
- “99% HEPA”.
These words refer to filters that fall short of the HEPA specification. Additionally, the majority of these filters are not independently evaluated. The HEPA standard is met by every HEPA filter, which has undergone independent testing.
Uses of High-efficiency particulate air Filter (HEPA)?
Application of HEPA includes:
- The HEPA filter is used to shield the drug products (FP & API) from air pollutants or air-borne particles.
- By employing it, product quality can be preserved.
- It is frequently used in the pharmaceutical, FMCG, military, biological, nuclear, and medical industries.
- In the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system used in Pharmaceuticals manufacturing units.
- Due of its very low air fiber release, high-efficiency particle air filters (HEPA) are safe to operate and have no overall negative consequences on human health.
- COVID-19: The SARS CoV2 is about 0.125 m. Even if SARS-CoV-2 droplets are on the floor, HEPA filters may be able to catch them in the air.
- Vehicle/ Car also uses HEPA purifier in body. Ex. Tesla Model X use HEPA filter
- Modern Airplanes use HEPA circulation to minimize the pathogen spread.
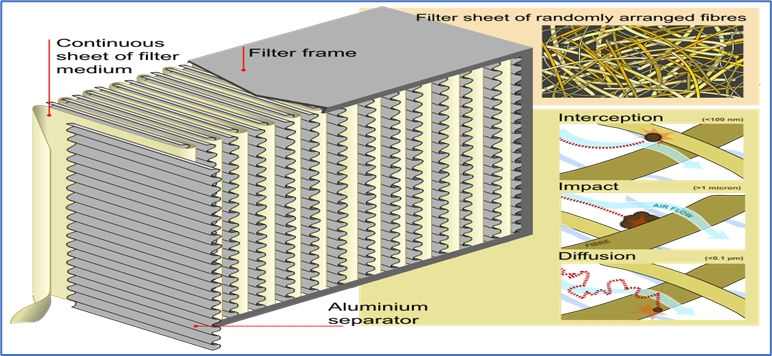
How do HEPA filters work? What are they made from?
MOC (Materials of Construction) of HEPA Filters is as per below,
- HEPA filters are made by or constructed of sheets of plastic fibers or borosilicate glass fibers (e.g., polypropylene).
- In the event of a hot zone or De-pyrogenetic circumstances, ceramic glass fiber is used. They are simple to clean. The filters should be cleaned with distilled water and then dried with air.
Mechanism of HEPA:
The mechanism of HEPA filters works in Four ways:
- Direct impaction
- Sieving
- Interception and
- Diffusion
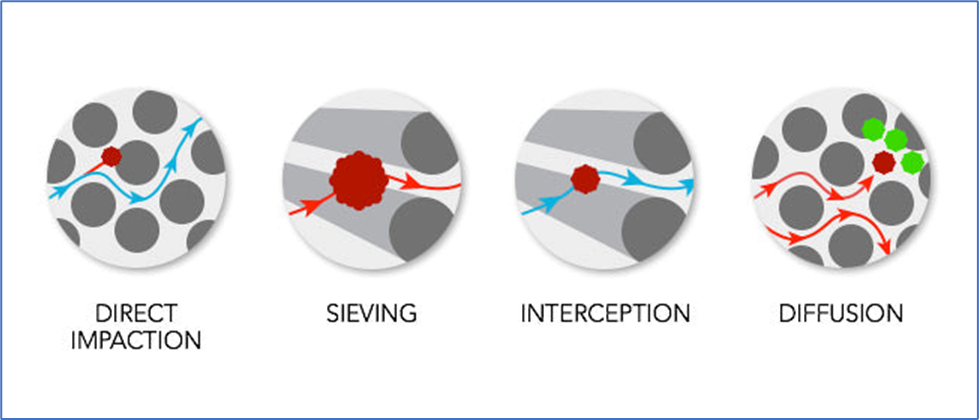
Direct Impaction:
- Large pollutants (below 0.3 μm ) go straight ahead, collide with a fibre, and adhere to it, including some types of large dust, mould, and pollen.
Sieving:
- A particle is transferred between two fibres by an air stream, but because it is larger than the gap, it got stuck.
Interception:
- Despite the ability of airflow to reroute around fibres, particles attach to the sidewalls of fibres due to inertia, which prevents them from doing so.
Diffusion:
- Small, ultra-fine particles are more likely to strike and adhere to fibres because they move more irregularly than bigger particles.
Construction of HEPA Filter (High efficiency particulate air filter):
HEPA and ULPA filters come in a variety of varieties. They can be grouped into a typical class based on efficiency, as indicated above, but they can also be divided based on how the filters are built. The following are some of the most typical building types:
Box / Rigid cell filter:
- Filters made of a rigid cell or a box and packed with filter media are referred to as box or rigid cell filters.
Cartridge filter:
- Filters with cylindrical housings and a fabric or paper filter cartridge are known as cartridge filters. Usually, the cartridge can be changed.
Fan filter:
- Lint and other large particles shouldn’t build up around the motor and fan with the use of fan filters made of fiberglass or mesh-like materials.
Filter mat:
- Filter mats are fiber-based filters that catch particles carried along in the flow of gas or air. Bulk rolls, pads, and reloadable frames are examples of common setups.
Panel filter:
- Panel filters are often made of mesh-like materials or fiberglass. They are made to stop lint and other big particles from building up in and around heating and ventilation systems.
Gas filtration
- HEPA filters are made to effectively stop very small particles, but they do not remove gases or odour molecules.
- When filtering volatile organic compounds, chemical vapours, or odours from pets, cigarettes, or flatulence, activated carbon (charcoal) or another type of filter should be used instead of or in addition to a HEPA filter.
- High efficiency gas adsorption filters (HEGA), or carbon cloth filters, are said to be several times more effective than granular activated carbon at adsorbing gaseous pollutants. They were initially developed by the British Armed Forces as a protection against chemical warfare.
Pre-filter and HEPA filter
- To increase the lifespan of the more expensive HEPA filter, a pre-filter—typically carbon-activated—can be used in conjunction with a HEPA bag filter.
- In such a system, the pre-filter serves as the initial stage of the filtering process, removing the majority of the bigger dust, hair, PM10, and pollen particles from the air.
- The pre-smaller filter’s particles are removed by the second stage high-quality HEPA filter. It frequently happens in air handling units.
Reference:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HEPA
- https://www.epa.gov/indoor-air-quality-iaq/what-hepa-filter
- https://www.iso-aire.com/blog/what-is-a-hepa-filter-and-how-does-it-work
- https://www.nafahq.org
- IEST RP-CC001 — HEPA and ULPA filters
- IEST-RP-CC007 — Testing ULPA filters
- ASTM F1471 — Standard Test Method for Air Cleaning Performance of a High-Efficiency Particulate Air Filter System
Read More:
- Types of chromatography
- CIP and SIP in Pharmaceuticals Positive control and negative control in Microbiology
- Types of biological indicators for sterilization
- Sterility Assurance Level (SAL) D value and Z values in Microbiology
- SOP on “Operation and Cleaning of Vertical Autoclave”
- Vacuum Leak Test, acceptance criteria and pharmaceutical applications
- Tablets Hardness Testing
- Water Hardness and Water Softening
- Microbiological Monitoring (RODAC Plates) Fluidized Bed Dryer (FBD): Principle, Working Process Tablets (Pharmacy)
- Pharmaceutical Powders: Definition, Classification and its Uses
- Preparation of Pharmaceutical Powders
- incorporation-of-ingredients-into-pharmaceutical-powders
- Classification of Tablet Coating
Definition
