Classification of Tablet Coating
Tablet coating is classified mainly into two types:
- 1. Sugar coating
- 2. Film coating
- Sub division:
- Non-enteric coating
- Enteric coating
A. Sugar Coating
The major ingredient used in sugar coating is sugar, which may be substituted by other materials like sorbitol. Other additives used are as follows:
- Fillers: contains calcium carbonate, talc and titanium dioxide.
- Coloring agents: FD&C approved dyes and lakes.
- Film formers: Acacia, gelatin and cellulose derivatives.
- Anti-adherents: Talc and surfactants.
- Flavouring agents: Fruit and chocolate flavors.
Different stages of sugar coating
1. Seal coating:
- Seal coating approach is used to cover (encapsulate) the core tablet with a layer of water-resistant polymer, preventing aqueous solvent from penetrating the core tablet during the primary coating phase.
- The core tablets are placed into the coating pan, subjected to dedusting, mainly with cellulose acetate phthalate solution spraying, and drying before being finished.
- The asbestos-free talc is applied on the seal-coated pills, and they are rotated for 3 to 5 minutes.
- The machinery is turned off, and the tablets are dried for an hour while the exhaust is turned on and cool air is supplied.
- Ingredients: Mainly Cellulose acetate phthalate, shellac, acetone and ethanol .
2. Sub-coating:
- This Sub-coating process is done to advance the bond between seal coat and the sugar coat by means of water-soluble polymer.
- The tablets are rotated and the sub-coating solution (like: acacia) is sprayed over the tablets after which the tablets are rotated for 15 min. with purified talc (if necessary)
- Ingredients includes: Acacia, puri.water gelatin, Powder sugar cane.
3. Syruping:
The next three steps comprise this process :
- Grossing:
- The exhaust is turned “ON” before the pills are introduced. A 120 °F or such temperature of warm air is passed.
- Sub-coating agents are present in the solution that is sprayed. The tablets are rolled for 15 to 30 minutes after coating.
- Ingredients: Sub-coating agent, coloring agent, sugarcane powder and puri. water.
- Heavy syrup:
- In this step, the tablet gains the most weight. At a constant temperature and relative humidity, a syrup comprising a coloring ingredient and sugar cane powder is sprayed slowly and uniformly onto the tablets.
- To ensure tackiness, the pills are totally dried.
- Ingredients: Sugarcane powder, coloring agent and syrup.
- Regular syrup:
- In this step, distilled water is used to dissolve the colouring agent and sugar cane powder, which is then sprayed onto the tablet at a predetermined temperature.
- The entire batch is then left overnight with the pan’s lid snugly shut.
- Ingredients: Puri. water, colouring agent, and powdered sugarcane.
- Polishing:
- The coated tablets are rotated and the solution of polishing agents (like: bees wax) are sprinkled gradually and homogeneously, and after the process the tablets are rotated for a period of 30 min. by passing cold air in the machine.
- Ingredients: White beeswax, carnauba wax, ethanol and acetone.
Advantages of Seal coating
- Patients generally accept sugar-coated pills.
- The raw resources are affordable and widely accessible.
Disadvantages of Seal coating
- The cost of packaging and delivery goes higher as a result of the finished product’s increased weight and size (up to 40% of the weight of its core tablet).
- It is a very tedious and time-consuming operation.
- No engraving or monogramming of the tablet is allowed.
- A highly trained coating operator is required.
B. Film Coating
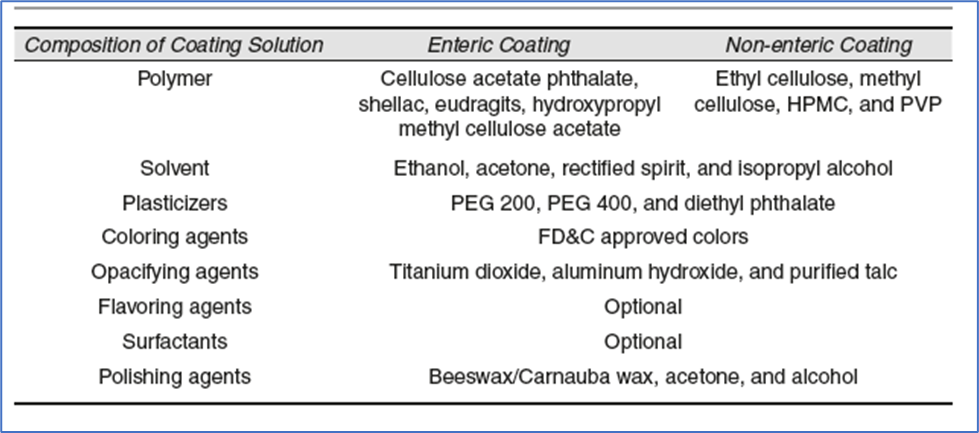
The composition of a coating solution is explained in below Table,
Advantages of Film Coating
- Reduction in coating time and material cost.
- No significant rise in tablet weight.
- Seal coating is not required.
- No. of coating steps is less.
- It resists cracking and chipping.
Disadvantages of Film Coating
- It has a high risk of flammability hazards.
- It will add concern over environmental pollution.
Methods of tablet coating
Methods of tablet coating are as follows:
- Pan coating
- Air suspension coating
- Dip coating
- Compression coating
Related: Enteric coated tablets
Reference:
- Tablet Coating – an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
- Book: Arun S. Mujumdar (2015). Handbook of Industrial Drying. CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, New York.
- Book: PHARMACEUTICAL ENGINEERING-Principles and Practice Unit Operations Abridged with PCI Syllabus of B. Pharmacy by C.V.S. Subrahmanyam, J. Thimmasetty, Mrs Sarasija Suresh and Mrs V. Kusum Devi
Read More:
- Pharmaceutical Powders: Definition, Classification and its Uses
- Preparation of Pharmaceutical Powders
- Types of chromatography
- CIP and SIP in Pharmaceuticals
- Positive control and negative control in Microbiology
- Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
- Type of Capsules
- Tablets Defects
- Tablet Friability
- Thin Layer Chromatography
