Disintegration Test:
- Disintegration is the process of breaking down tablets into granules or smaller particles.
- The time it takes for a tablet to disintegrate is measured using a device outlined in the USP/NF.
- A disintegration test is a measurement of how long it takes for a batch of tablets to break up into particles under specific conditions.
- This test is required for all tablets intended for oral administration, with the exception of those that are designed to be chewed before swallowing or those that should dissolve slowly in the mouth, such as lozenges and effervescence tablets.
- Disintegration time: Time required for breaking of the tablet into small particles under influence of disintegrating fluid.
- Disintegrating fluid:
A. 0.1 M Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
B. Water
C. Simulated gastric fluid (SGF)
D. Simulated intestinal fluid (SIF).
Disintegration Test Apparatus:
A. Circular basket rack assembly:
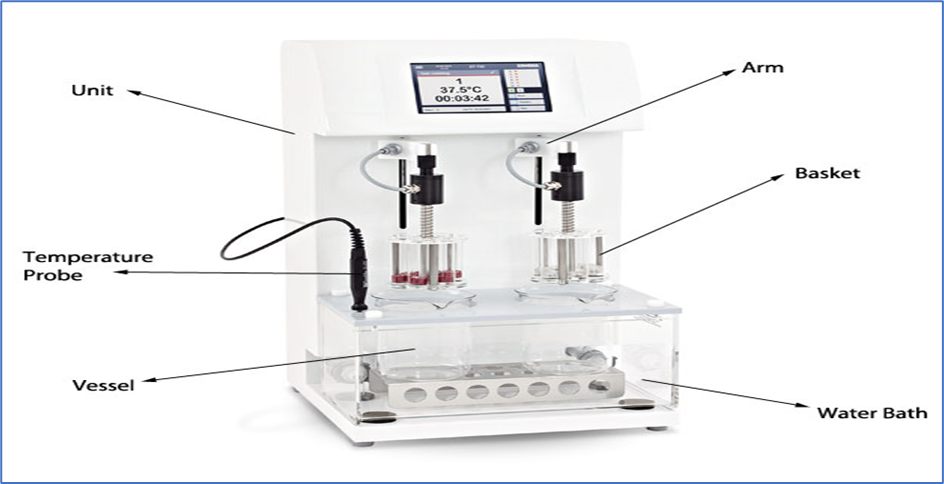
- For the immersion fluid, a 1000 mL low-form beaker with an internal diameter of 97–115 mm and a height of 138–160 mm is suitable.
- Thermostatic arrangement for maintaining the temperature at 37±2°C
- A device for raising and lowering of basket rack in immersion fluid at a constant frequency of 28 to 32 cycles/min through a distance of 2.5 cm below the liquid surface and 2.5 cm above the surface of the beaker bottom.
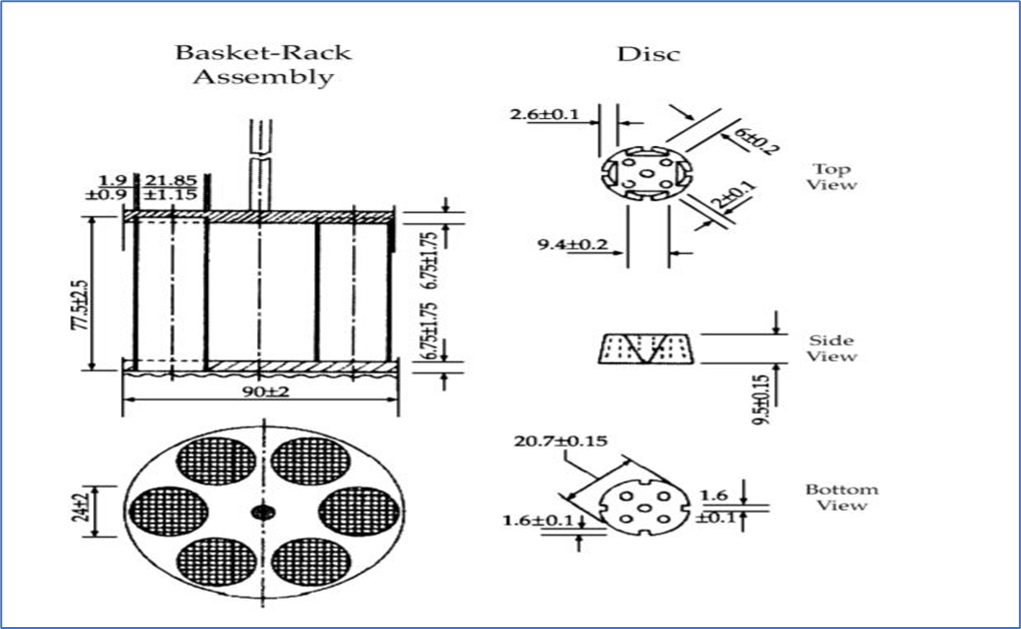
B. Basket-rack assembly:
- The basket-rack assembly contains of 6 open-ended transparent tubes and a rack for holding these tubes in a vertical (Upright) direction.
- Each tube is 75.0 to 80.0 mm (3 inches) long with an internal diameter of 20.7 to 23 mm, 1.0 to 2.8 mm thickness and open at the top, and 10 mesh (1.8-2.2 mm) screen at the bottom end.
- The tubes are held in a vertical position by two plastic plates which are circular in shape and made up of transparent material having six holes of a diameter that allow the tube to be inserted.
- The basket-rack assembly is suspended from the raising and lowering device at a point on its axis using a suitable manner.
- A perforated disc is used to keep the tablet inside the tubes during the process.
Disintegration Apparatus:

Disintegration Test Procedure:
| Uncoated or Plain-Coated Tablets* | Delayed-Release Tablets (DR) and Capsules | Effervescent Tablets for Oral Solution | Effervescent Granules | |
| Test Procedure | Place 1 dosage unit in each of the 6 tubes of the basket | Place 1 dosage unit in each of the 6 tubes of the basket | Place 1 tablet in each of 6 beakers containing | 1 dose of the effervescent granules |
| Media | Water or the specified medium as the immersion fluid | Acid stage Immersion fluid: 0.1 M HCl, or simulated gastric fluid TS, or as specified in the monograph Buffer Stage: Immersion fluid: 1. pH 6.8 phosphate buffer, or 2. Simulated intestinal fluid (SIF) TS, or 3. As specified in the monograph | 200 mL of water. A beaker with a notional volume of 250–400 mL will suffice. | 200 mL of water. A beaker with a notional volume of 250–400 mL will suffice. |
| Temperature | 37 ± 2°C | 37 ± 2°C | 37 ± 2°C | 37 ± 2°C |
| Time | As per Monograph | Acid: 1hr Buffer: As per Monograph | 5 min or as specified in the individual monograph | As per Monograph |
*Buccal Tablets, Sublingual Tablets, Capsules, Tablets for Oral Suspension, Tablets for Oral Solution, Tablets for Topical Solution, Orally Disintegrating Tablets, and Chewable Tablets- same criteria
Acceptance Criteria:
- All 6 tablets or capsules should be disintegrated.
- If 1 or 2 dosage unit/s fail to disintegrate then repeat the test with additional 12 tablets.
- The requirements of the test are met if NLT 16 of the 18 (6+12) dosage units tested are disintegrated.
Read More:
Peak Purity
Dissolution and Sinkers
Analytical Instrument Category
GAMP Guideline
Tablet Scoring or Splitability study or Breakability Test
Difference between Suspension and Emulsion
Size, Shape, and other Physical Attributes of Generic Tablets and Capsules
For Acronyms and Abbreviations
Reference:
USFDA: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents
EMA: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory/research-development/scientific-guidelines
MHRA: https://www.gov.uk/government/organisations/medicines-and-healthcare-products-regulatory-agency
